Description of indicators
Web Metrics is a new initiative pioneered by Google to provide a unified guide to Web quality signals that are critical to delivering a great user experience on the Web.
Over the years, Google has provided a number of performance measurement and performance tools. Some developers are adept reporting at using these tools, while others find the sheer number of tools and metrics overwhelming.
Site owners do not need to be performance experts to understand the quality of experience they are providing to users. The Web Metrics Program is designed to simplify scenarios and help websites focus on the most important metrics, namely Core Web metrics.
Core Web metrics
Core Web Metrics are a subset of Web metrics that apply to all Web pages, that every website owner should measure, and that will also be displayed in all Google tools. Each core Web metric represents a different aspect of the user experience, can be measured in practice, and reflects the true experience of key user-centric outcomes.
The constituent metrics of the core Web metrics evolve over time. The current composition of metrics for 2020 focuses on the three aspects Loading performance of the user experience, Interactivity and Visual stability, and includes the following metrics (and their corresponding thresholds):
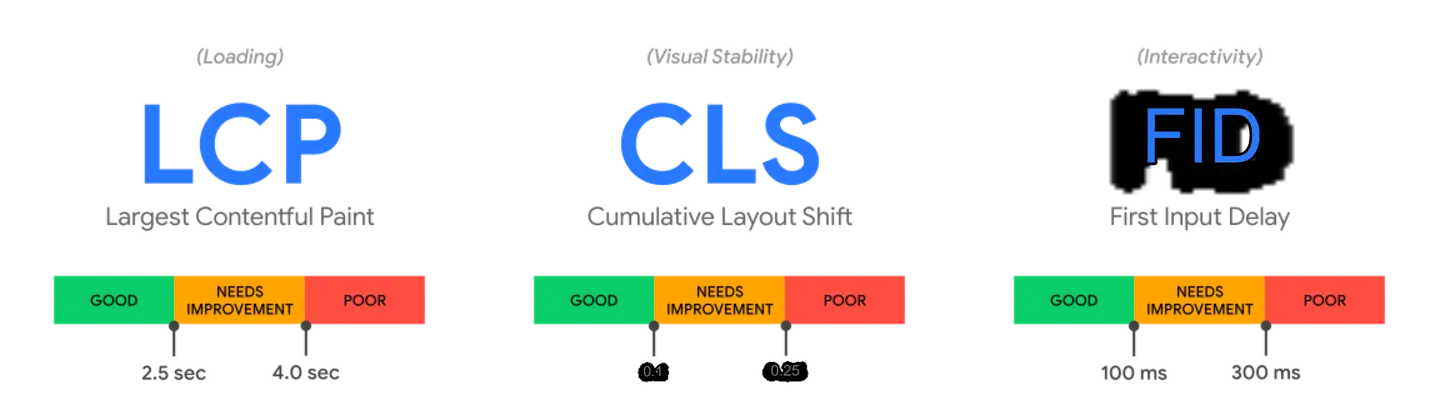
- Largest Contentful Paint (LCP): Maximum content drawing, measuring Load performance. To provide a good user experience, the LCP should occur within days after 2.5 seconds the page first starts loading.
- First Input Delay (FID): First input delay, measured Interactivity. In order to provide a good user experience, the FID of the page should be 100 milliseconds or shorter.
- Cumulative Layout Shift (CLS): Cumulative layout offset, measured Visual stability. In order to provide a good user experience, the CLS of the page should be kept at 0.1 or less.
To ensure that you can achieve the recommended target values during the majority of user visits, a good measurement threshold for each of the above metrics is page-loaded 75th percentile and applies to both mobile and desktop devices.
If a page meets the 75th percentile of the recommended target values for all three metrics above, the tool that evaluates compliance with the core Web metrics should judge the page as passing.
Page performance monitoring
| Indicator | Description | Calculation Formula |
|---|---|---|
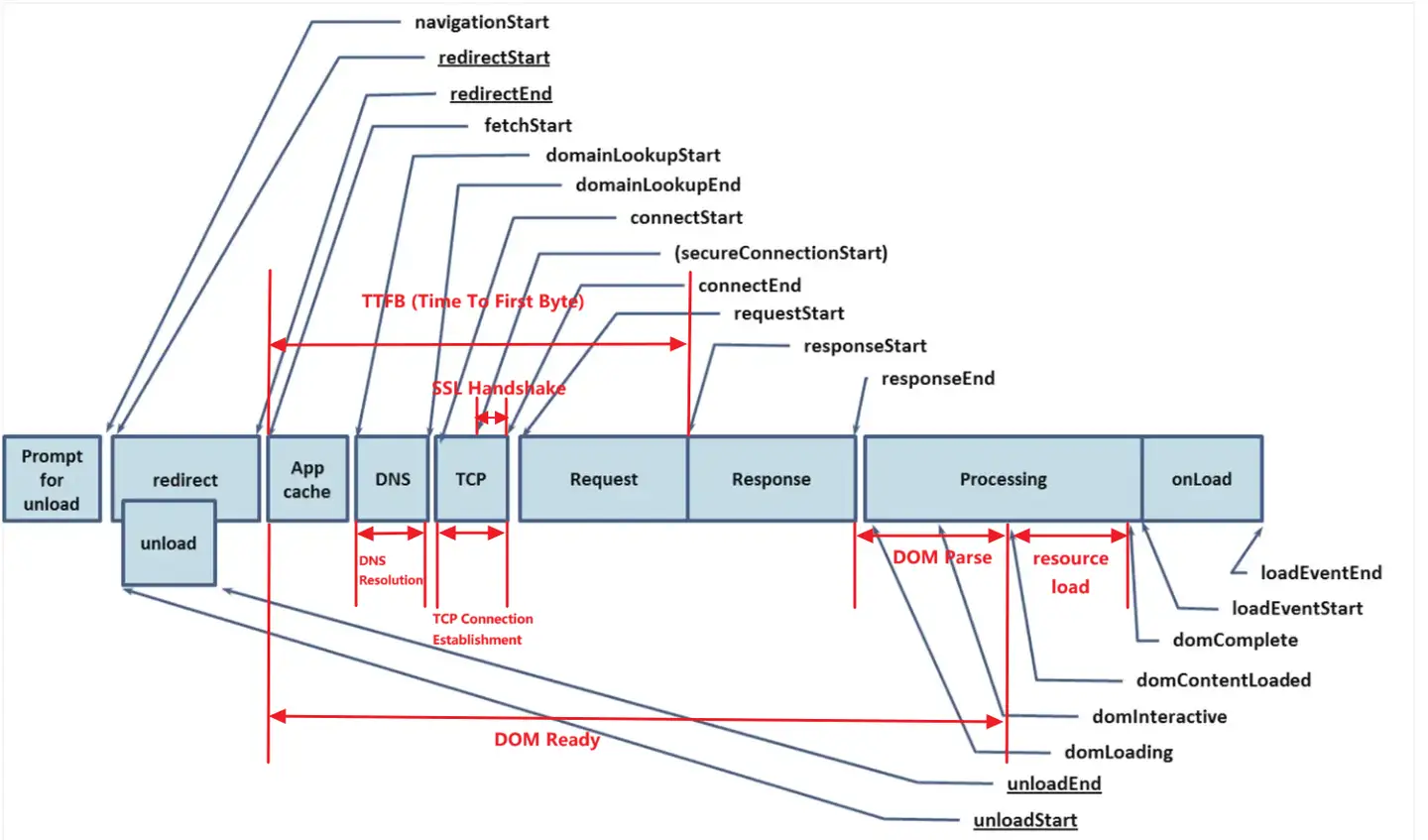
| TTFB | Time To First Byte, that is, the time taken for the first byte of the network request, from sending the page request to receiving the first byte of the response data | responseStart - fetchStart |
| FCP | First Contentful Paint, that is, the first time there is content rendering. In the performance statistics, the time from the time when the user starts to visit the Web page to the time point of FCP can be regarded as the time without content, that is, in the process of accessing the Web page, before the time point of FCP, the user sees a screen without any actual content, and the user can not obtain any useful information at this stage | fp - fetchStart where fp gives priority to using the browser PerformanceObserver to listen to the 'first content paint' event |
| LCP | Largest Contentful Paint, that is, the maximum content painting time, is the Core Web Vitals metric used to measure when the largest content element in the viewport is visible. It can be used to determine when the main content of the page will be rendered on the screen | fs - fetchStart where fs takes priority to use the last LCP time before the full load event is triggered, and LCP uses the browser PerformanceObserver to listen to the 'largest content paint' event |
| CLS | Cumulative Layout Shift, that is, cumulative layout offset, is a measure of the maximum layout change score for every unexpected layout change that occurs in the entire life cycle of a page | Use the browser PerformanceObserver to listen to the 'layout shift' event |
| FID | First Input Delay, that is, the first input delay, measures the delay time of the user's first interaction with the page. It is the time from the user's first interaction with the page to the time when the browser can really start processing the event handler to respond to the interaction | Use the browser PerformanceObserver to listen to the 'first input' event |
| TTI | Time to Interactive, that is, the fully interactive time, is a non-standard Web performance "progress" indicator, defined as the time point when the last "long task" completed, followed by 5 seconds of inactivity of the network and the main thread. | - |
| TBT | Total Blocking Time, that is, the total blocking time. It is a measure of the total time between FCP and TTI. During this period, the main thread is blocked for too long to make input responses | Total time of all long tasks from FCP to TTI exceeding 50ms |
| LoadEventEnd | End of loading event | loadEventEnd - fetchStart where loadEventEnd uses performance.timing.loadEventEnd |
| Fully loaded | After the loadEventEnd is completed, the time until the response to the Ajax requests and static resource requests initiated within a period of time (500ms by default) can be regarded as the time taken for the page to fully load. | - |
| DCL | DOMContentLoaded, which measures the time when the browser is ready to execute any client script. DCL refers to the time when the browser has assembled the DOM (document object model) and no stylesheet prevents JavaScript from executing during the web page loading process | domContentLoaded - fetchStart |
| Redirect | If redirection does not occur, or one of the redirects is not from the same source, the value is 0 | redirectEnd - redirectStart |
| DNS | Time consuming for domain name resolution (0 when hit the resolution cache) | domainLookupEnd - domainLookupStart |
| TCP | TCP connection takes time | connectEnd - connectStart |
| SSL | The SSL secure connection takes time | secureConnectionStart = 0 ? 0: connectEnd - secureConnectionStart |
| Request | After the SSL connection is established, the first response from the client to the server takes time | responseStart - requestStart |
| Response | Time consuming from the first response of the server to the full response of the data | responseEnd - responseStart |
Page analysis indicators
| Indicator | Description | Calculation formula |
|---|---|---|
| Number of slow pages | Page visits exceeding the slow page threshold. | Page visits exceeding the slow FCP threshold + exceeding the slow LCP threshold + exceeding the slow DCL threshold + exceeding the slow full load threshold |
| Slow page ratio | The ratio of page visits exceeding the slow page threshold to the total visits. | (Page visits exceeding the slow threshold (slow FCP, slow LCP, slow DCL, slow full load) / total visits) * 100% |
| Number of users affected by slow pages | UVs with slow pages | - |
Operation analysis indicators
| Indicator | Description | Calculation formula |
|---|---|---|
| Number of operations | The number of times an operation is requested. | An operation is requested once and recorded once. |
| Operation time | The time when the operation is completed. | When the operation is an Ajax request, the end time of the last Ajax of the multiple Ajaxs corresponding to the operation - the start time of the first Ajax. When the operation is a page, the completion time of the FCP/LCP/DCL/full load indicators of the user-defined page is the operation time. |
| Operation availability | The ratio of successful operations to the total number of operations. | (Successful operations/Total operations)*100% |
| Operation request time | The projection time of the request corresponding to the operation. | - |
| Average server time | The time from the server receiving the request to the completion of processing. | - |
User analysis indicators
| Indicator | Description |
|---|---|
| PV | Page View, page visits. |
| UV | User View, user visits. |
| Session | User session visits, from entering the page to closing the page as a session. |
JS error indicators
| Indicator | Description |
|---|---|
| Number of JS errors | Number of PVs with JS errors |
| JS error rate | Number of PVs with JS errors/Total PV |
| Number of users affected | Number of UVs with JS errors |
Request analysis indicators
| Indicator | Description |
|---|---|
| Response time | Time from when a request is issued to when the server returns and receives the returned result |
| Number of requests | Number of requests to access the application |
| Slow request ratio | Number of requests exceeding the slow request threshold/Total number of requests reported |
| Number of users affected by slow requests | UVs with slow requests |
| Error rate | Number of requests with status code 400 or above/Number of requests |
| Number of users affected by errors | Number of UVs with request errors |